How a Capacitor is Charged?
Capacitors play a vital role in various electronic circuits, allowing for the storage and release of electrical energy. Understanding how a capacitor is charged is essential for anyone interested in electronics or seeking to delve into circuit design. In this article, we will explore the process of capacitor charging, its underlying principles, and its applications.
Introduction
When it comes to electronic circuits, capacitors serve as fundamental components that store and release electrical energy. Whether it's in power supplies, timing circuits, or filtering applications, capacitors are integral to their proper functioning. To comprehend the charging process, we first need to grasp the basic principles of capacitors.
What is a Capacitor?
▷ Basic Structure
A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. The conductive plates, typically made of metal, are electrically insulated from each other, but they can store opposite charges. The dielectric material, often made of ceramic, plastic, or electrolyte, prevents direct contact between the plates while allowing an electric field to form between them.
▷ Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in various types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Some common types include electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, tantalum capacitors, and film capacitors. The choice of capacitor type depends on factors such as capacitance, voltage rating, temperature stability, and cost.
Understanding Capacitor Charging
To comprehend how a capacitor is charged, we need to grasp the concepts of voltage and current in relation to capacitors and the process of charging and discharging.
▷ Voltage and Current
Voltage represents the electrical potential difference between two points, and it is necessary for charging a capacitor. Current, on the other hand, is the flow of electric charge and is involved in both the charging and discharging of a capacitor. Understanding these principles is crucial to understanding the charging process.
▷ Charging and Discharging
When a voltage is applied across the terminals of a capacitor, it begins to charge. The charging process involves the accumulation of charge on the plates, leading to a potential difference between them. Conversely, discharging occurs when the stored charge in the capacitor is released, causing the potential difference to decrease.
How a Capacitor is Charged
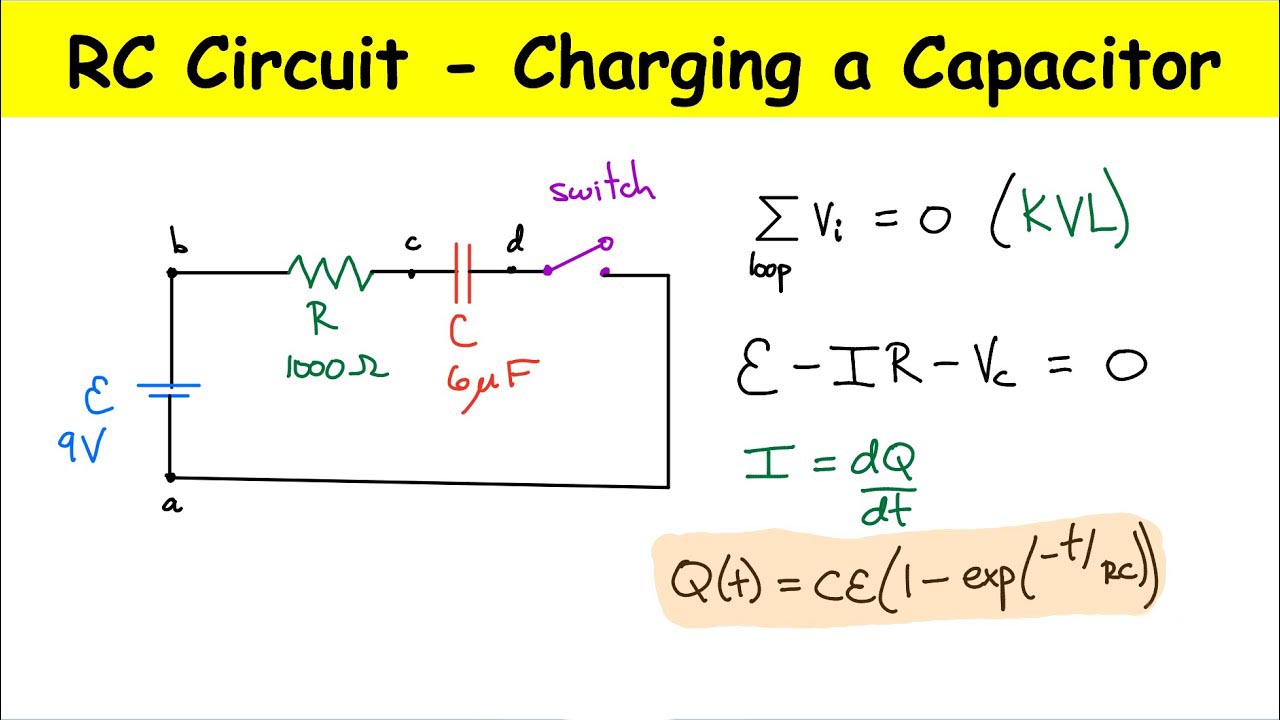
▷ Charging Process
The charging process of a capacitor can be divided into three stages: initial, intermediate, and final. Initially, when a voltage is applied, the capacitor behaves as a short circuit, and a surge of current flows through it. As time progresses, the current decreases, and the voltage across the capacitor gradually rises. In the final stage, the capacitor becomes fully charged, and the current ceases to flow.
▷ Capacitance and Charge Storage
The capacitance of a capacitor determines its ability to store charge. Capacitance is influenced by factors such as the surface area of the plates, the distance between them, and the dielectric material used. A higher capacitance allows for greater charge storage and an increased energy storage capacity.
▷ Time Constants
Time constants play a crucial role in capacitor charging. They represent the time required for a capacitor to charge or discharge to a specific percentage of its total voltage. The time constant is determined by the product of capacitance and the resistance through which the capacitor is charging or discharging.
Applications of Capacitor Charging
Capacitor charging finds applications in numerous electronic devices and circuits. It is used in power supply circuits to smooth out fluctuations and provide a stable voltage output. Timing circuits utilize capacitors to control the duration of events. Additionally, capacitors play a role in filtering circuits to remove unwanted noise or signals.
Factors Affecting Capacitor Charging
Several factors influence the charging process of capacitors. These factors can be categorized into capacitor properties and external factors.
▷ Capacitor Properties
Capacitor properties such as capacitance, voltage rating, and internal resistance affect the charging process. Higher capacitance values lead to slower charging, while higher voltage ratings determine the maximum voltage that can be applied across the capacitor. Internal resistance influences the charging time and can lead to power dissipation.
▷ External Factors
External factors include the applied voltage, the resistance in the circuit, and the presence of other components. These factors impact the charging time and the behavior of the capacitor within the circuit.
Safety Considerations
When working with capacitors, it is essential to take appropriate safety precautions. Capacitors can store electrical energy even after power is disconnected, posing a risk of electric shock. Discharging capacitors properly, avoiding high voltages, and following safety guidelines are vital to ensure personal safety.
Conclusion
Understanding how a capacitor is charged is crucial for anyone working with electronic circuits. The charging process involves the accumulation of charge on the conductive plates of a capacitor, leading to the creation of a potential difference. Capacitor charging finds applications in various electronic circuits and devices, playing a vital role in their proper functioning.
9. FAQs
Q1. Can a capacitor be overcharged?
Yes, a capacitor can be overcharged if a voltage higher than its rated voltage is applied. This can lead to capacitor failure or even an explosion in extreme cases.
Q2. How long does it take to charge a capacitor fully?
The time it takes to charge a capacitor fully depends on factors such as capacitance, applied voltage, and the resistance in the circuit. It can range from a fraction of a second to several minutes.
Q3. Can I discharge a capacitor by shorting its terminals?
Discharging a capacitor by shorting its terminals is a common method. However, caution should be exercised to avoid potential dangers, such as electric shocks.
Q4. Can a charged capacitor shock you?
Yes, a charged capacitor can deliver a harmful electric shock. It is crucial to discharge capacitors properly before working with them to ensure personal safety.
Q5. What happens if a capacitor is connected in reverse polarity?
Connecting a capacitor in reverse polarity can lead to excessive current flow, overheating, and potential damage to the capacitor. It is important to observe the correct polarity when connecting capacitors in a circuit.



