Can Capacitor Convert AC to DC?
In the world of electronics, the conversion of alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) is a common requirement. Many electronic devices and appliances, from power supplies to electronic gadgets, operate on DC power. While there are several methods and components available for AC-to-DC conversion, the question arises: can a capacitor convert AC to DC? In this article, we will delve into the working of capacitors, their behavior in AC and DC circuits, and ultimately address the possibility of using capacitors for AC-to-DC conversion.
AC and DC are two fundamental forms of electric current. AC, as the name suggests, periodically changes its direction, while DC flows consistently in one direction. Most power grids supply electricity in the form of AC, but many electronic devices require DC for their operation. This necessitates the need for AC-to-DC conversion.
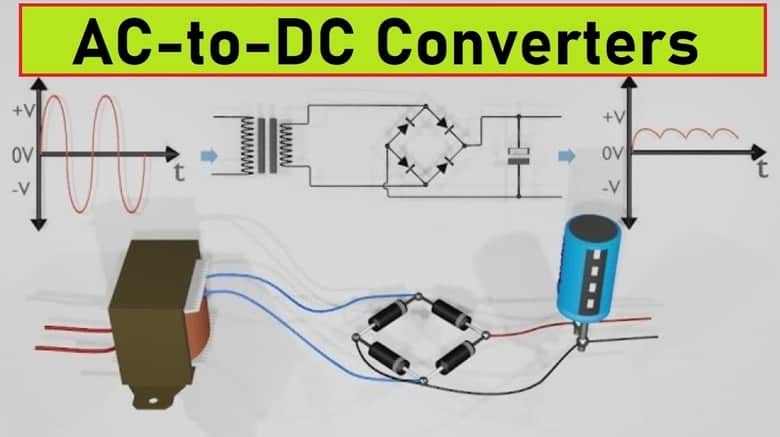
Understanding AC and DC
To understand AC-to-DC conversion, it is essential to grasp the differences between AC and DC currents. AC is characterized by its continuous change in direction, cycling back and forth within a circuit. In contrast, DC maintains a constant flow in a single direction. AC voltages are typically represented as sinusoidal waves, whereas DC voltage remains constant.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic component widely used in various circuits. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the capacitor, it stores electrical charge on its plates, which can be discharged when needed. Capacitors come in different types and capacitance values, allowing for versatile applications in electronics.
How does a Capacitor Work?
The working principle of a capacitor revolves around its ability to store and release electrical charge. When a voltage is applied across a capacitor, one plate accumulates positive charge while the other plate accumulates negative charge. This separation of charge creates an electric field between the plates, resulting in the storage of energy. When the voltage source is removed, the capacitor can discharge the stored energy.
Capacitor in AC Circuits
In an AC circuit, the behavior of a capacitor is distinct. As the AC voltage alternates its polarity, the capacitor charges and discharges accordingly. During each half-cycle, the capacitor charges as the voltage rises and discharges as the voltage falls. This property allows capacitors to store and release energy in synchronization with the AC signal, leading to various applications such as power factor correction and energy storage.
Capacitor in DC Circuits
In a DC circuit, the role of a capacitor is different compared to an AC circuit. When connected to a DC source, the capacitor charges until the voltage across it reaches the same potential as the source. Once charged, the capacitor acts as an open circuit, preventing further current flow. However, when the DC source is removed or fluctuates, the capacitor discharges its stored energy to compensate for the change in voltage.
Can Capacitor Convert AC to DC?
While capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, they cannot directly convert AC to DC. A capacitor alone cannot alter the direction of current flow. Its primary function is to store and release energy. To convert AC to DC, additional components and techniques are required.
The Capacitor as a Voltage Regulator
Although a capacitor cannot convert AC to DC, it can serve as a vital component in AC-to-DC conversion circuits. In power supplies, capacitors are often used as voltage regulators. They help smooth out voltage fluctuations by storing energy during the peak periods of an AC cycle and releasing it during the troughs. This process reduces the ripple voltage and ensures a more stable DC output.
Applications of Capacitors in AC-to-DC Conversion
Capacitors find significant applications in AC-to-DC conversion circuits. One common use is in rectifiers, which convert AC to pulsating DC. Capacitors are employed in combination with rectifier diodes to smoothen the pulsations and provide a more steady DC output. Additionally, capacitors are used in filter circuits to further reduce ripple voltage and ensure a cleaner DC signal.
Limitations of Capacitor in AC-to-DC Conversion
While capacitors play a crucial role in AC-to-DC conversion, they do have limitations. One limitation is voltage ripple, which refers to the residual AC component present in the converted DC signal. Capacitors can reduce ripple, but they cannot eliminate it entirely. Additionally, capacitors may incur power loss due to their equivalent series resistance (ESR), reducing overall efficiency. Another limitation is the handling of high-power applications, as capacitors may not be able to handle high currents efficiently.
Alternatives to Capacitor in AC-to-DC Conversion
When capacitors are insufficient for a particular AC-to-DC conversion scenario, alternative components and techniques can be employed. Rectifier diodes, for example, can convert AC to DC by allowing current flow in one direction while blocking the opposite direction. Transformers are another alternative, enabling efficient voltage conversion through electromagnetic induction. In more advanced applications, switching power supplies employ semiconductor devices to achieve precise and efficient AC-to-DC conversion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, capacitors are remarkable components with diverse applications in electronics. While they cannot directly convert AC to DC, they play an important role in AC-to-DC conversion circuits as voltage regulators, rectifier filters, and energy storage elements. Understanding the behavior and limitations of capacitors in AC and DC circuits is crucial for efficient and reliable power supply design. When faced with the task of AC-to-DC conversion, it is essential to explore alternative components and techniques that offer more efficient and precise conversion.
FAQs
Can a capacitor alone convert AC to DC?
No, a capacitor alone cannot convert AC to DC. It can only store and release energy but cannot change the direction of current flow.
What are the applications of capacitors in AC-to-DC conversion?
Capacitors are commonly used in rectifiers and filter circuits to convert AC to DC and smooth out voltage fluctuations.
What are the limitations of using capacitors for AC-to-DC conversion?
Capacitors have limitations such as voltage ripple, power loss, and inability to handle high-power applications efficiently.
What are the alternatives to capacitors in AC-to-DC conversion?
Alternatives include rectifier diodes, transformers, and switching power supplies, which offer more efficient and precise AC-to-DC conversion.
Are there any specific safety considerations when working with capacitors in AC-to-DC conversion circuits?
Yes, it's important to follow proper safety measures, such as discharging capacitors before handling them and using appropriate voltage ratings for capacitors.



