Do All AC Motors Need a Capacitor?
Do All AC Motors Need a Capacitor?
AC motors are widely used in various applications, from powering industrial machinery to running household appliances. They provide the necessary rotational motion required for many devices. But have you ever wondered if all AC motors require a capacitor? In this article, we'll delve into the world of AC motors and explore the role of capacitors in their operation.
AC motors, or alternating current motors, are electrical devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. They rely on the principles of electromagnetism to generate rotational motion. Unlike DC motors, AC motors are more commonly used due to the widespread availability of AC power.
What is an AC Motor?
Before we discuss the need for capacitors in AC motors, let's first understand how these motors work. AC motors consist of two main components: a stator and a rotor. The stator contains windings that produce a rotating magnetic field when an alternating current is passed through them. The rotor, on the other hand, is the part that rotates in response to the magnetic field.
Types of AC Motors
There are several types of AC motors, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include induction motors, synchronous motors, and brushed and brushless DC motors. In this article, we'll primarily focus on induction motors, as they are the most widely used in various industries.
Role of Capacitors in AC Motors
☆ Understanding Capacitors
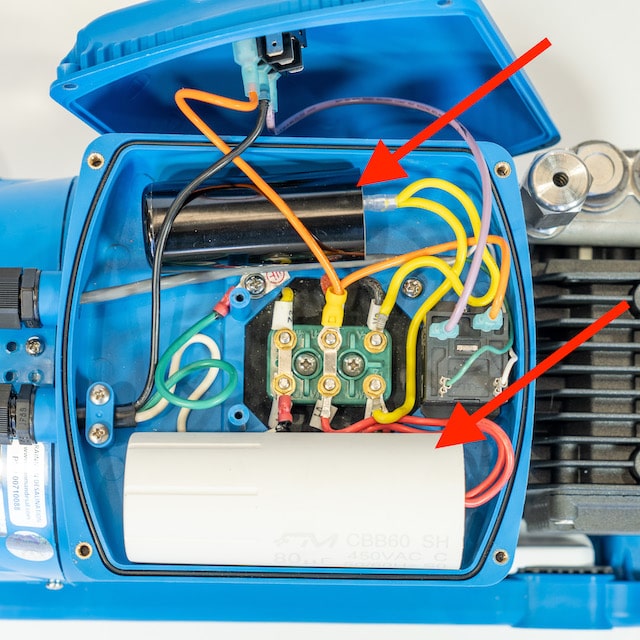
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, the capacitor charges and stores energy. Capacitors are commonly used in electrical circuits to perform various functions.
☆ Starting Capacitors
In AC motors, starting capacitors are used to provide an additional phase shift to the motor windings during startup. This phase shift helps create the necessary torque to initiate rotation. Once the motor reaches its operating speed, the starting capacitor is disconnected from the circuit.
☆ Running Capacitors
Unlike starting capacitors, running capacitors are used in AC motors to improve their efficiency and power factor during operation. These capacitors remain connected to the motor circuit throughout its runtime, providing the necessary reactive power to optimize motor performance.
Capacitor Start Induction Run (CSIR) Motors
☆ Working Principle
One type of AC motor that requires a capacitor is the Capacitor Start Induction Run (CSIR) motor. This motor utilizes a starting capacitor during startup to provide the required phase shift for initiating rotation. Once the motor reaches a specific speed, a centrifugal switch disconnects the starting capacitor, allowing the motor to continue running using only the running winding.
☆ Advantages and Disadvantages
The CSIR motor design is relatively simple and cost-effective, making it suitable for many applications. However, it has a lower starting torque compared to other types of motors and can experience higher power consumption during startup.
Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motors
☆ Working Principle
Another type of AC motor that uses a capacitor is the Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor. In this motor, a running capacitor is connected in series with the auxiliary winding. The capacitor and winding create a phase shift, which produces a rotating magnetic field necessary for motor operation. PSC motors are commonly used in applications where a moderate starting torque is required.
☆ Advantages and Disadvantages
PSC motors offer improved efficiency and higher power factor compared to CSIR motors. They also have a relatively simple design and lower starting current. However, they may have a lower starting torque compared to other motor types.
Capacitor-Start Capacitor-Run (CSCR) Motors
☆ Working Principle
Capacitor-Start Capacitor-Run (CSCR) motors are another type of AC motor that utilizes capacitors. These motors have two capacitors: a starting capacitor and a running capacitor. The starting capacitor provides the initial phase shift during startup, and the running capacitor remains connected to the circuit throughout the motor's runtime.
☆ Advantages and Disadvantages
CSCR motors offer improved starting torque compared to CSIR and PSC motors. They are commonly used in applications where a higher starting torque is required, such as air compressors and certain types of pumps.
Capacitor Selection for AC Motors
The selection of capacitors for AC motors depends on various factors, including motor design, application requirements, and power supply characteristics. It is essential to choose the right capacitance and voltage rating to ensure proper motor operation and longevity.
Do All AC Motors Need a Capacitor?
Not all AC motors require capacitors. The need for capacitors depends on the motor type, application, and design. Motors like CSIR, PSC, and CSCR motors rely on capacitors for starting, improved efficiency, and power factor correction. However, some types of AC motors, such as shaded pole motors and some types of synchronous motors, do not require capacitors for their operation.
Factors Affecting the Use of Capacitors
☆ Motor Design
Different motor designs have varying requirements when it comes to capacitors. Factors such as the number of winding phases, rotor design, and desired starting torque play a role in determining whether a motor requires a capacitor or not.
☆ Application Requirements
The specific application and load characteristics also influence the need for capacitors in AC motors. Some applications may require higher starting torque or improved efficiency, making the use of capacitors necessary.
Consequences of Operating AC Motors without Capacitors
Operating AC motors without the required capacitors can lead to various consequences. These include reduced starting torque, increased power consumption, decreased motor efficiency, and potential motor damage due to excessive heat generation.
Common Issues with Capacitors in AC Motors
Capacitors in AC motors can sometimes experience issues such as capacitor failure, reduced capacitance, or increased leakage current. These issues can affect motor performance and should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Capacitor-related Problems
If you encounter capacitor-related issues in an AC motor, it is important to troubleshoot and diagnose the problem accurately. This may involve checking the capacitance, leakage current, and visual inspection of the capacitor. In cases of capacitor failure, it is necessary to replace the faulty capacitor with a new one.
Conclusion
In conclusion, not all AC motors require capacitors. The need for capacitors depends on the motor type, design, and application requirements. Capacitors play a crucial role in motors like CSIR, PSC, and CSCR motors by providing the necessary starting torque, improving efficiency, and power factor correction. However, other motor types may operate without capacitors. It is essential to consider motor design and application characteristics when determining the need for capacitors.
FAQs
Q: Can I replace a faulty capacitor in an AC motor myself?
A: It is recommended to consult a qualified technician or electrician to replace a faulty capacitor in an AC motor. Working with electrical components can be dangerous, and it is important to ensure proper safety measures are taken.
Q: Are there any safety concerns when dealing with capacitors in AC motors?
A: Yes, capacitors can store electrical charge even when the power is disconnected. It is crucial to discharge the capacitor properly and follow safety guidelines to prevent electrical shocks.
Q: Can a motor run with a faulty capacitor?
A: Depending on the motor type and design, a faulty capacitor can affect motor performance. It may result in reduced starting torque, increased power consumption, or motor overheating.
Q: How long do capacitors typically last in AC motors?
A: The lifespan of capacitors in AC motors can vary depending on several factors, including usage conditions, temperature, and quality of the capacitor. On average, capacitors can last between 10 to 20 years.
Q: Are there any alternatives to capacitors for AC motors?
A: Yes, in some cases, motor manufacturers may incorporate alternative technologies like electronic soft starters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) to achieve the desired motor performance without capacitors.



