5 Health Benefits of Pears
5 Health Benefits of Pears
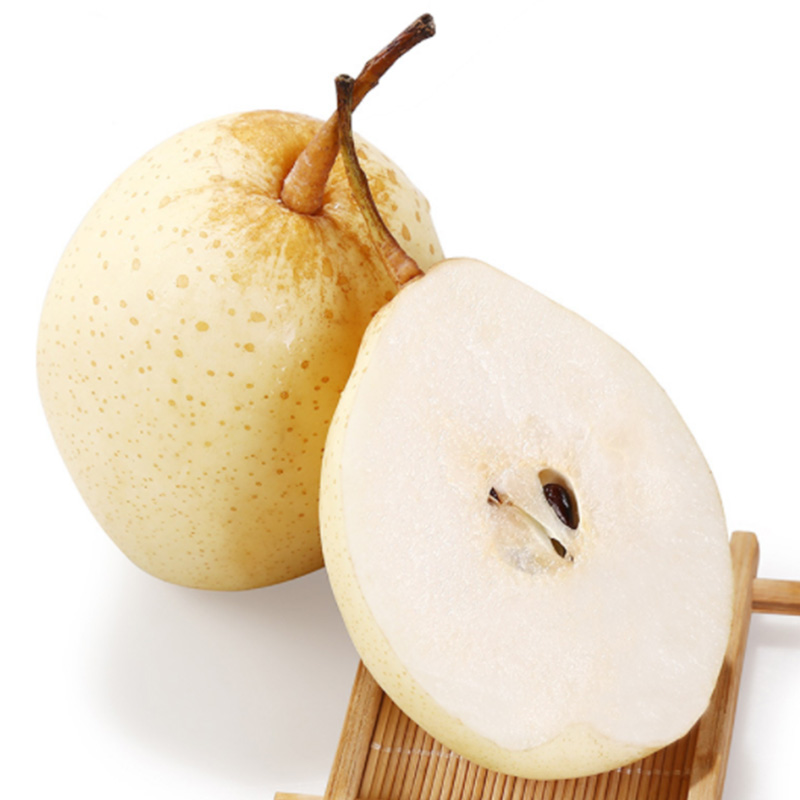
Ironically, not every pear is 'pear-shaped.' One variety, Asian pears, is actually shaped like an apple. But no matter their shape, all pears are rich in disease-fighting nutrients.
Link to Guowang
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
'Pears are so healthy, and most people tolerate them very well,' says registered dietitian Beth Czerwony, RD, LD. 'They're terrific for your digestion and have other impressive health benefits. They're a perfect snack if you're craving something sweet.'
Types of pears
Pears are members of the Rosaceae plant family, along with apples, apricots, cherries, peaches and several other fruits and berries. Pears can range in texture, color, crispness, juiciness and sweetness. Common varieties you may find in the grocery store include:
- Anjou (green or red).
- Asian.
- Bartlett.
- Bosc.
- Comice.
- Concorde.
- Forelle.
- Seckel.
- Starkrimson.
Health benefits of pears
Are pears good for you? Absolutely. Pears are a great source of antioxidants, fiber, potassium and vitamin C. But they're not just full of nutrients ' they also may lower your risk of some diseases. Here are five ways pears boost your health.
1. A nutritious source of vitamins and minerals
Like most fruit, pears are a source of good nutrition. One medium pear has approximately:
- 102 calories.
- 27 grams of carbohydrates.
- 0 grams of cholesterol.
- 0.2 grams of fat.
- 6 grams of fiber.
- 0.6 grams of protein.
- 1 milligram of sodium.
- 17 grams of sugar.
A medium pear also gives you:
- 8 milligrams of vitamin C (9% daily value or DV).
- 8 micrograms of vitamin K (7% DV).
- 0.05 milligrams of vitamin B6 (5% DV).
- 206 milligrams of potassium (4% DV).
Advertisement
2. Helps manage your blood sugar
Nobody enjoys the dreaded crash that happens after sugary foods spike your blood glucose. Steady blood sugar means a steady supply of energy, which is healthier for your body. Blood sugar management is even more important if you have diabetes.
Czerwony says pears may help stabilize blood sugar and even reduce your risk of Type 2 diabetes. How? Fiber, for starters. A medium pear offers nearly one-quarter of the fiber you need in a day. Fiber helps keep blood sugar steadier by slowing your body's absorption of sugar.
Pears also contain anthocyanin, an antioxidant. An observational study suggests a link between eating anthocyanin-rich foods and a lower risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Another study showed that eating pears could significantly lower your odds of developing Type 2 diabetes. For each serving of pears eaten per week, researchers found a 3% lower risk of Type 2 diabetes.
In addition, pears are a low-glycemic food, which means they won't spike your blood sugar like sugary foods and some fruits can.
3. Relieves constipation and improves digestive health
Fiber adds bulk to and softens your stool, which helps things move along in your gut. Lots of foods contain fiber, but pears are a particularly excellent source.
A single pear contains 6 grams of fiber (more than 20% of what an adult needs in a day). And pectin, a type of fiber in pears, has some specific benefits. Pectin is a soluble fiber known to help:
- Constipation: In a study of 80 people with constipation, pectin significantly improved food movement through their digestive systems and reduced symptoms.
- Gut microbiome: Pectin promotes the growth of good bacteria in your colon, according to a review of several studies, helping your microbiome stay healthy.
To reap the fibrous benefit of pears, don't skip the skin. 'Pear skin contains a significant amount of the fruit's total fiber content,' notes Czerwony.
4. Lowers inflammation
Inflammation happens when your immune system tries to protect you from something ' an infection, a toxin or some other offender. Some temporary inflammation is actually a healthy response to these things. But when inflammation hangs around, it can contribute to diseases such as Alzheimer's, asthma, cancer and Type 2 diabetes.
Antioxidants are nutrients that can prevent some of the cell damage that leads to inflammation. Pears are rich in powerful types of antioxidants called flavonoids.
Research shows that flavonoids can reduce inflammation and lower the risk of:
- Cancer.
- Heart disease.
- Infections from bacteria, fungi and viruses.
- Alzheimer's disease, dementia and Parkinson's disease.
- Stroke.
- Type 2 diabetes and the nerve damage it can cause.
5. Promotes heart health
Pears are an excellent part of a heart-healthy diet. Nutrients in pears that can benefit your heart include:
Advertisement
In addition, a study examining the effects of fruit and vegetable consumption suggests eating pears lowers your risk of stroke. And one large clinical trial showed a link between eating pears and a lower risk of dying from heart disease.
Are fresh, canned or frozen pears better?
'In general, fresh fruits are best because they have the highest amount of nutrients,' explains Czerwony. 'Frozen is usually a close second to fresh. The heat of canning, though, can break down certain nutrients.'
But don't avoid canned pears completely. They're still good for you. She advises looking for pears in water rather than syrup, which adds unneeded sugar.
'You might be surprised by what you can do with fresh pears,' she adds. 'Think of how you use apples ' sliced raw, in pies or baked ' and you can do all those things with pears.'
Try making this poached pear dessert, include pears in your stuffing or make some interesting salads with pears.
Advertisement
9 Health and Nutrition Benefits of Pears
Pears are rich in nutrients and several beneficial plant compounds. They may also help promote weight loss and protect against certain chronic conditions.
Pears are sweet, bell-shaped fruits that have been enjoyed since ancient times. They can be eaten crisp or soft.
They're not only delicious but also offer many health benefits backed by science.
Here are 9 impressive health benefits of pears.
Share on Pinterest
Linda Raymond/Getty Images1. Highly nutritious
Pears come in many different varieties. Bartlett, Bosc, and D'Anjou pears are among the most popular, but around 100 types are grown worldwide (1).
A medium-sized pear provides the following nutrients (2):
- Calories: 101
- Protein: 1 gram (g)
- Carbs: 27 g
- Fiber: 6 g
- Vitamin C: 9% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Vitamin K: 7% of DV
- Potassium: 4% of the DV
- Copper: 16% of DV
This same serving also provides small amounts of folate, provitamin A, and niacin. Folate and niacin are important for cellular function and energy production, while provitamin A supports skin health and wound healing (3, 4, 5).
Pears are likewise a rich source of important minerals, such as copper and potassium. Copper plays a role in immunity, cholesterol metabolism, and nerve function, whereas potassium aids muscle contractions and heart function (1, 6, 7, 8).
What's more, these fruits are an excellent source of polyphenol antioxidants, which protect against oxidative damage. Be sure to eat the whole pear, as the peel boasts up to six times more polyphenols than the flesh (9, 10).
summaryPears are especially rich in folate, vitamin C, copper, and potassium. They're also a good source of polyphenol antioxidants.
2. May promote gut health
Pears are an excellent source of soluble and insoluble fiber, which are essential for digestive health. These fibers help maintain bowel regularity by softening and bulking up stool (11, 12).
One medium-sized pear packs 6 g of fiber, or about 21% of your daily fiber needs (2).
Additionally, pears are rich in pectin, a type of soluble fiber that has been associated with several benefits, including improved gut health and immune function (13, 14).
Notably, pectin may also help relieve constipation. In one older 4-week study, 80 adults with constipation received 24 g of pectin per day. They experienced constipation relief and increased levels of beneficial gut bacteria (15).
As pear skin contains a substantial amount of fiber, it's best to eat this fruit unpeeled (11).
summaryAdditional reading:Pears offer dietary fiber, including prebiotics, which promotes bowel regularity, constipation relief, and overall digestive health. To get the most fiber from your pear, eat it with the skin on.
Aerosil 300 Hydrophilic Fumed Silica Flour 10Kg ...
Colloidal Silica - A Versatile Problem Solver, Product Article
Questions You Should Know about cassette seal manufacturer
Bamboo Slicer - Bamboo Cutter Latest Price, ...
Continuous Syringe Market 2024 | Expected to Grow at a ...
How Does teething toy Work?
What is dispersible polymer powder?
Are you interested in learning more about Chinese Fresh Pear Piece? Contact us today to secure an expert consultation!
3. Contain beneficial plant compounds
Pears offer many beneficial plant compounds that give these fruits their different hues.
For instance, anthocyanins lend a ruby-red hue to some pears. These compounds may improve heart health and protect against cancer (11, 16).
Though specific research on pear anthocyanins is needed, numerous population studies suggest that a high intake of anthocyanin-rich foods like berries is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease (17).
Pears with green skin feature lutein and zeaxanthin, two compounds necessary to keep your vision sharp, especially as you get older (2, 18).
Again, many of these beneficial plant compounds are concentrated in the skin (11).
summaryPears harbor many beneficial plant compounds. Those in red pears may protect heart health, while those in green pears may promote eye health.
4. Have anti-inflammatory properties
Although inflammation is a normal immune response, chronic or long-term inflammation can harm your health. It's linked to certain illnesses, including heart disease and type 2 diabetes (19).
Pears are a rich source of flavonoid antioxidants, which help ease inflammation and may decrease your risk of disease (11, 20).
Several large reviews tie high flavonoid intake to a reduced risk of diabetes and developing or dying from heart disease. This effect may be due to these compounds' anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (21, 22, 23).
What's more, pears pack several vitamins and minerals, such as copper and vitamins C and K, which also combat inflammation (6, 24, 25).
summaryPears are a rich source of flavonoids, which are antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation and protect against certain diseases.
5. May offer anticancer effects
Pears contain various compounds that may exhibit anticancer properties. For example, their anthocyanin and chlorogenic acid contents have been shown to protect against cancer (11, 26, 27, 28).
A few studies indicate that diets rich in fruits, including pears, may protect against some cancers, including those of the lung and stomach (29, 30).
What's more, some population studies suggest that flavonoid-rich fruits like pears may also safeguard against breast and ovarian cancers (31, 32).
While eating more fruit may reduce your cancer risk, more research is needed. Pears should not be considered a replacement for cancer treatment.
summaryPears contain many potent plant compounds that may have cancer-fighting properties. However, more research is needed.
6. Linked to a lower risk of diabetes
Pears ' particularly red varieties ' may help decrease diabetes risk.
One large older study in over 200,000 people found that eating five or more weekly servings of anthocyanin-rich fruits like red pears was associated with a 23% lower risk of type 2 diabetes (34).
Additionally, a mouse study noted that plant compounds, including anthocyanins, in pear peel exhibited both anti-diabetes and anti-inflammatory effects (35).
What's more, the fiber in pears slows digestion, giving your body more time to break down and absorb carbs. This can also help regulate blood sugar levels (36).
summaryPears may help reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes due to their fiber and anthocyanin contents.
7. May boost heart health
Pears may help lower your risk of heart disease.
Their procyanidin antioxidants may decrease stiffness in heart tissue, lower LDL (bad) cholesterol, and increase HDL (good) cholesterol (37, 38, 39).
The peel contains an important antioxidant called quercetin, which is thought to benefit heart health by decreasing inflammation and reducing heart disease risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol levels (11, 40).
One study in 40 adults with metabolic syndrome ' a cluster of symptoms that increases your heart disease risk ' found that eating 2 medium pears each day for 12 weeks lowered heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure and waist circumference (41).
Another study in over 30,000 women revealed that every daily 80-g portion of fruit decreased heart disease risk by 6%'7%. For context, a medium pear weighs around 178 g (2, 42).
Furthermore, regular intake of pears and other white-fleshed fruits is thought to lower stroke risk. An older 10-year study in over 20,000 people determined that every 25 g of white-fleshed fruit eaten daily decreased stroke risk by 9% (43).
summaryPears are rich in potent antioxidants, such as procyanidins and quercetin, that can boost heart health by improving blood pressure and cholesterol. Eating pears regularly may also reduce stroke risk.
8. May help you lose weight
Pears are low in calories, high in water, and packed with fiber. This combination makes them a weight loss-friendly food, as fiber and water can help keep you full (44, 45).
When full, you're naturally less prone to keep eating.
In one 12-week study, 40 adults who ate two pears daily lost up to 0.3 inches (0.7 centimeters) off their waist circumference (41).
Plus, a study found that women who added three pears per day to their usual diet for 10 weeks lost an average of 1.9 pounds (0.84 kilograms) (44).
summaryEating pears regularly may help you feel full because of their high amounts of water and fiber. In turn, this may help you lose weight.
9. Easy to add to your diet
Pears are available year-round and easy to find in most grocery stores.
Eaten whole ' with a handful of nuts if you choose ' they make a great snack. It's also easy to add them to your favorite dishes, such as oatmeal, salads, and smoothies.
Popular cooking methods include roasting and poaching. Pears complement chicken or pork especially well. They likewise pair nicely with spices like cinnamon and nutmeg, cheeses like Gouda and brie, and ingredients like lemon and chocolate.
However you choose to eat them, remember to include the skin to get the most nutrients.
summaryPears are widely available and easy to add to your diet. You can eat them whole with the skin on or incorporate them into main dishes. These fruits are especially delicious when roasted or poached.
The bottom line
Pears are a powerhouse fruit, packing fiber, vitamins, and beneficial plant compounds.
These nutrients are thought to fight inflammation, promote gut and heart health, protect against certain diseases, and even aid weight loss.
Just be sure to eat the peel, as it harbors many of this fruit's beneficial compounds.
If you want to learn more, please visit our website Chinese Fresh Pear in Box.
Understanding Single Lip Oil Seals: A Guide
Weighing the Cost of Rockwool
Top 5 Benefits of Centrifugal Rock Wool Pipe You Must Know!
The Advantages of Employing a PE Film Coating Machine
How to Use Flexible Rubber Foam Sheets?
The Advantages of Employing a Tape Roll Slitter
Silica sol gel as salt bridge - Powered by XMB 1.9.11